根据模型获取边界路径并自动巡航
更新时间: 2025-08-19 14:10:45
项目里需要设置一段自动巡航的路径,然后摄像机跟着路径自动巡航,效果如下:
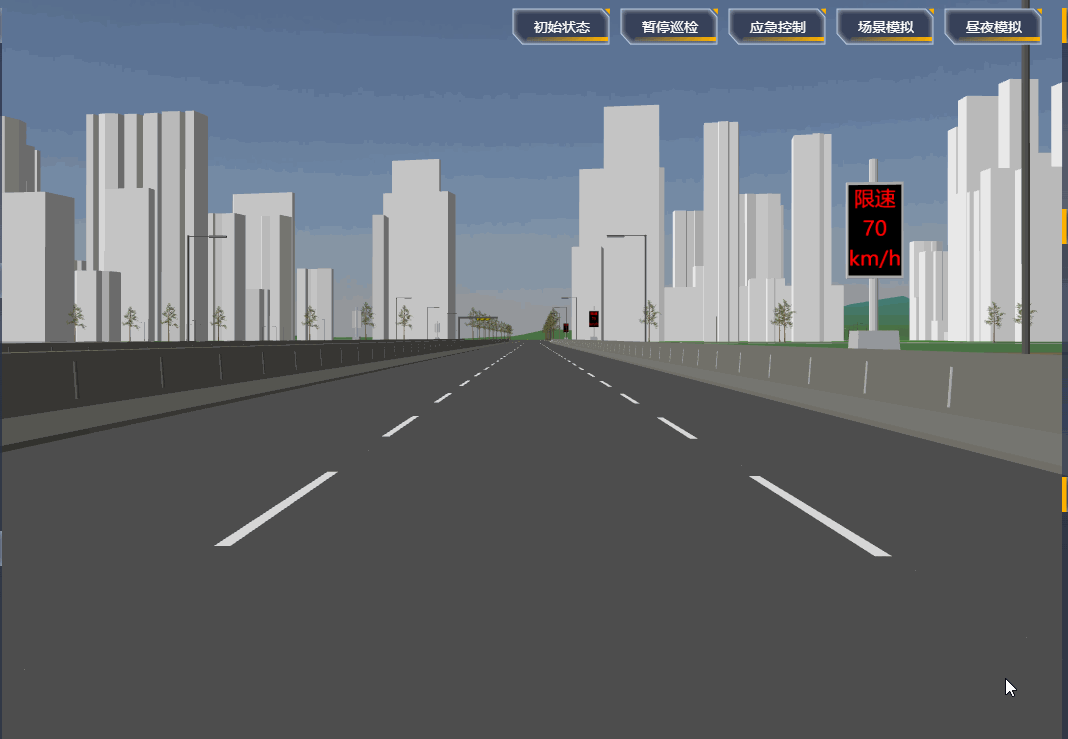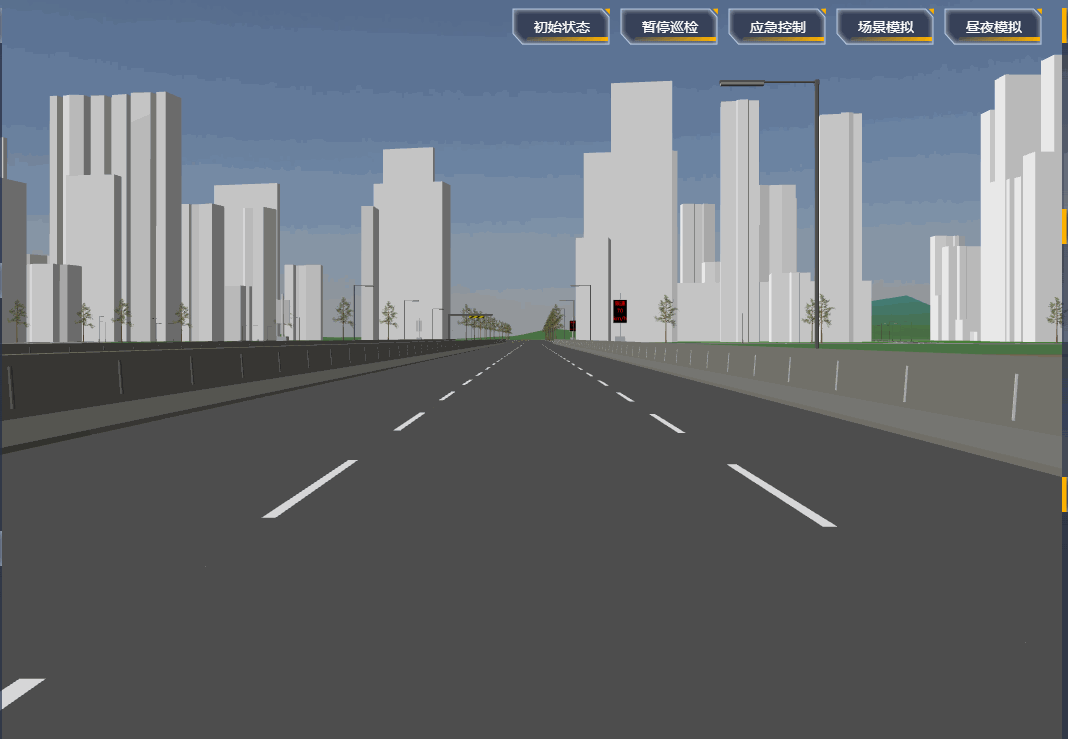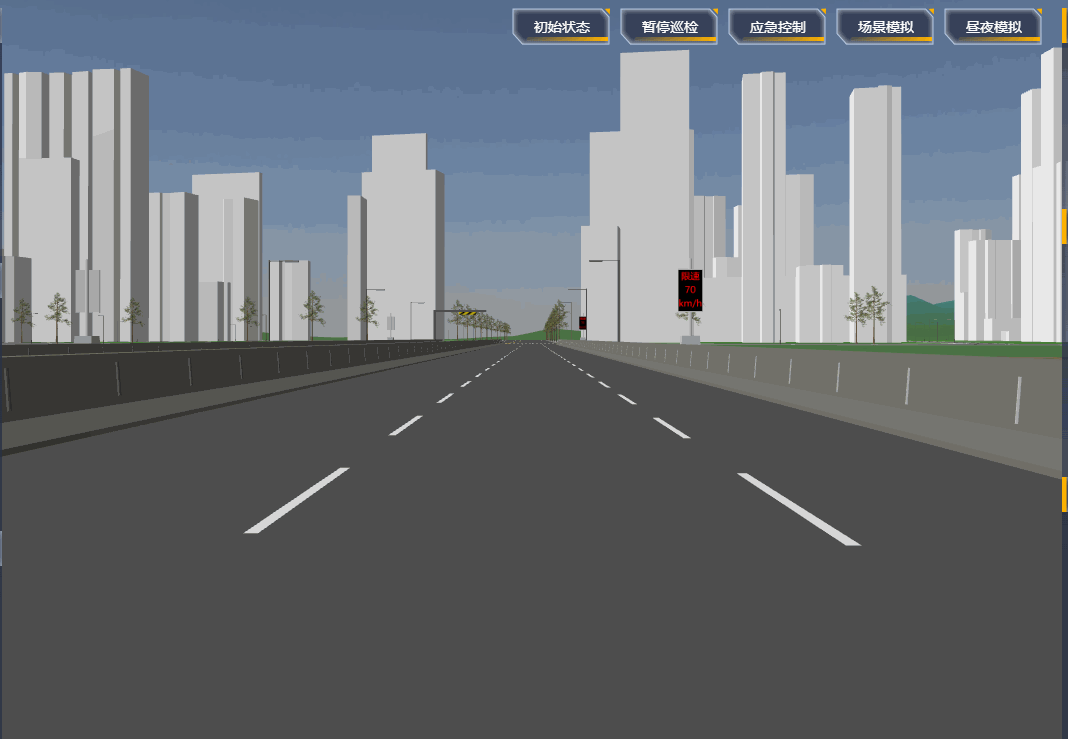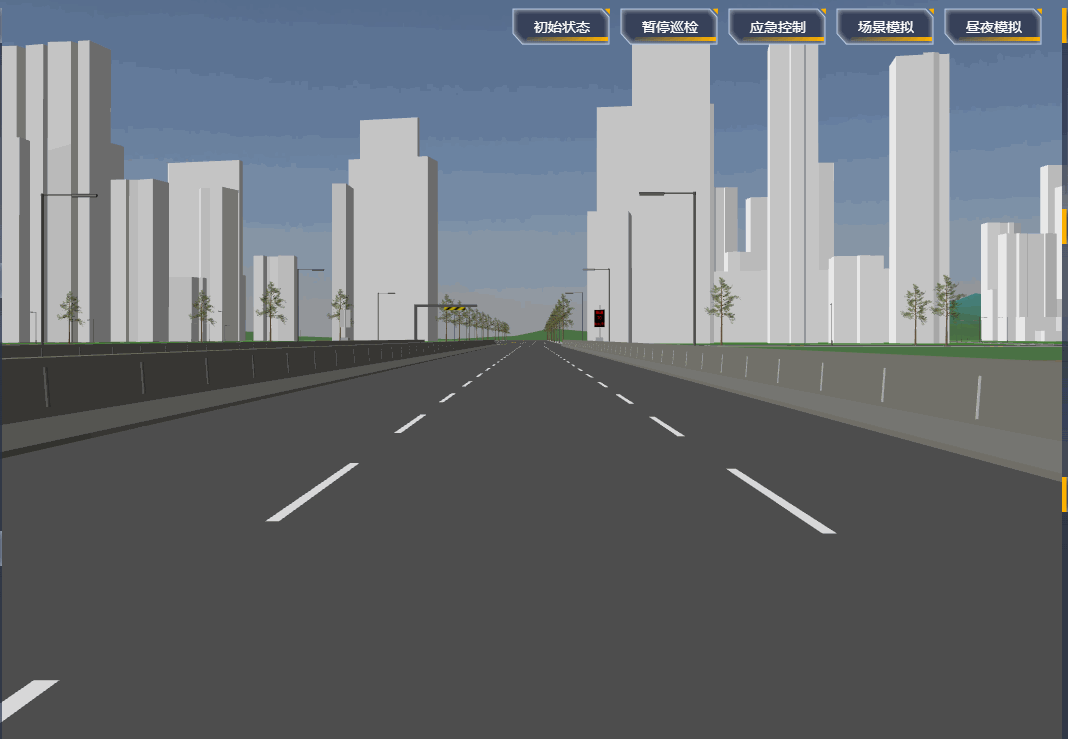
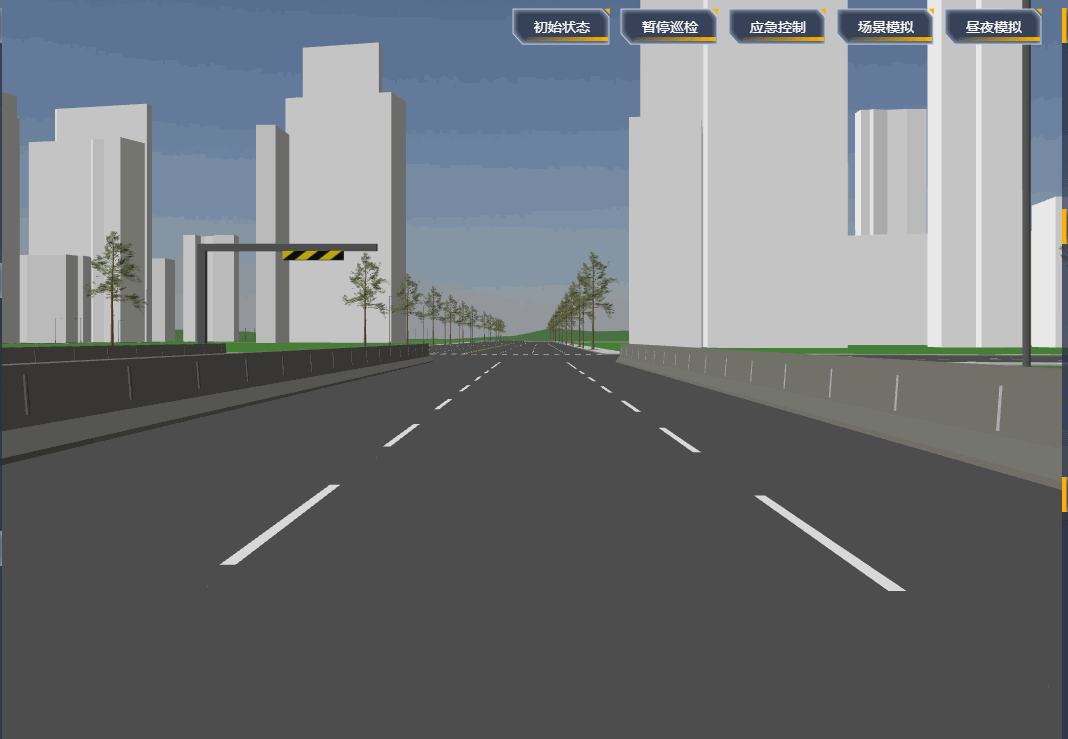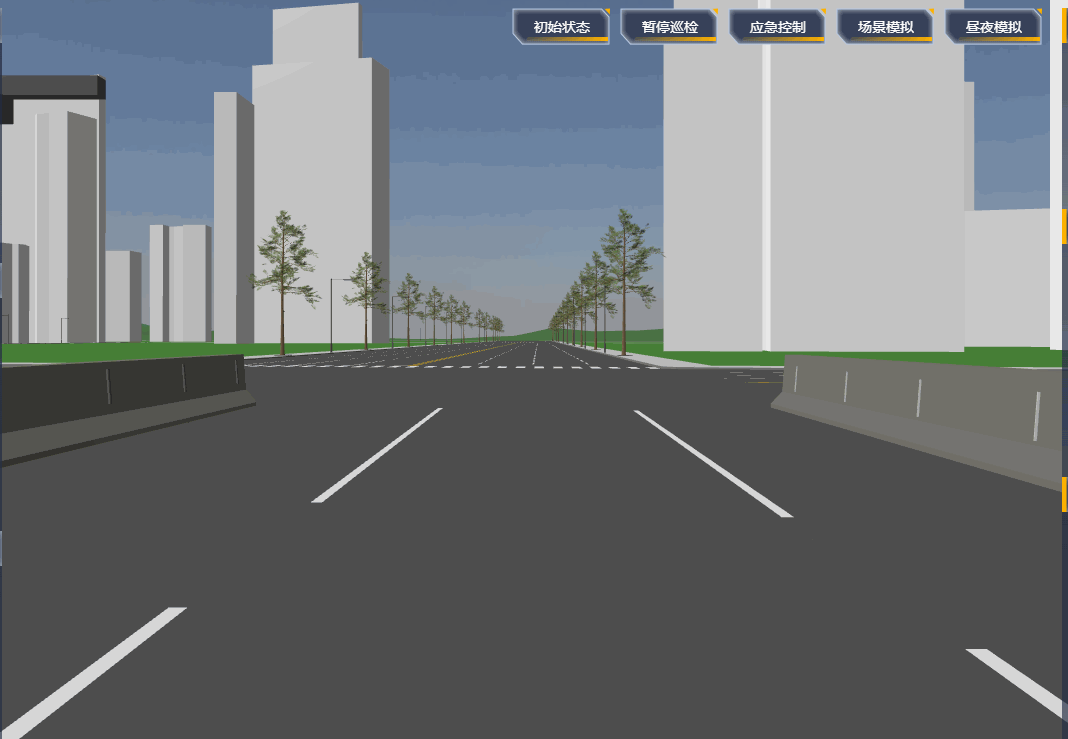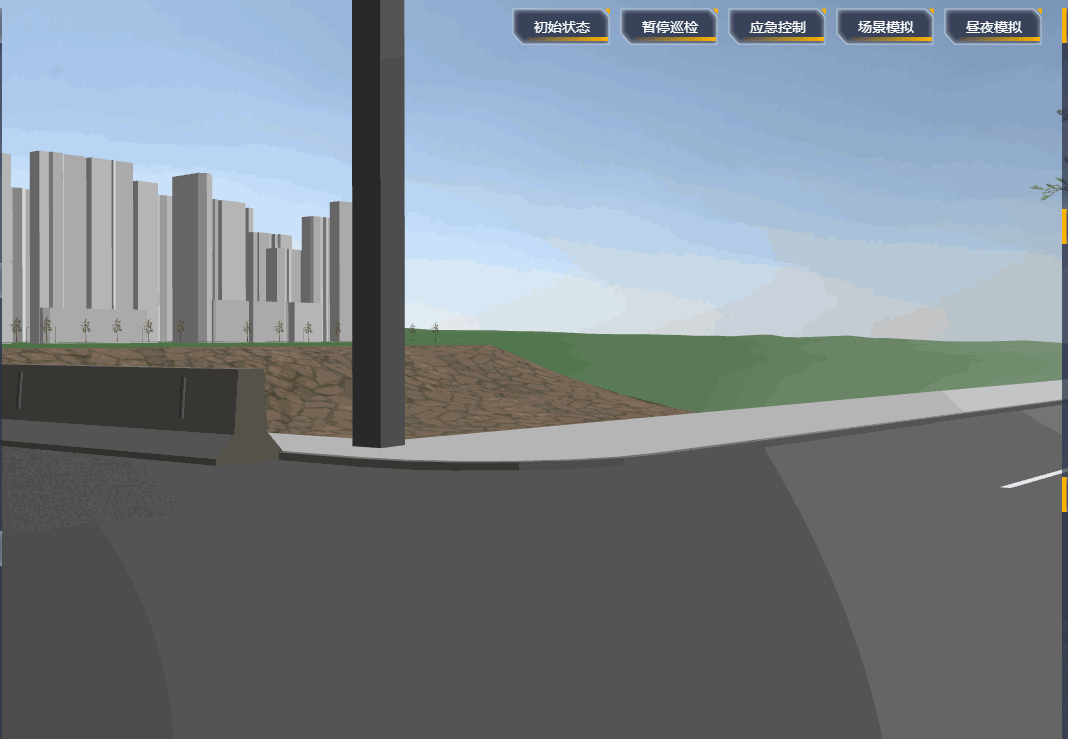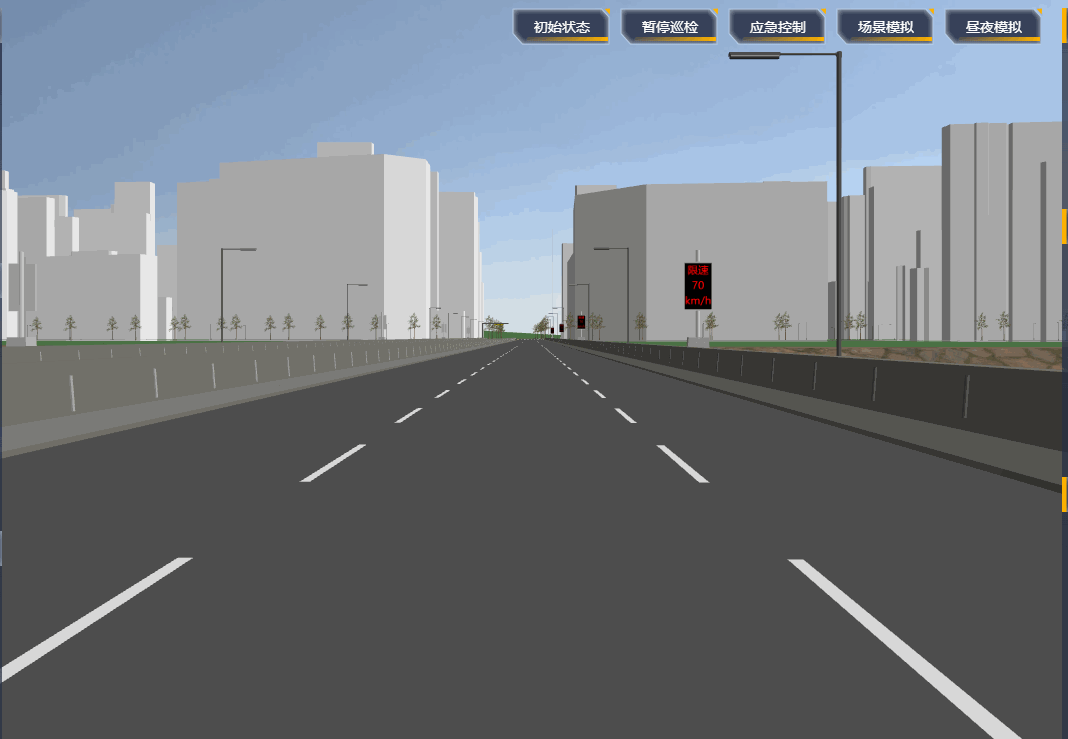
# 原理
因为路径自己找点的位置很麻烦,所以我使用贝塞尔曲线建了个模型,将模型分作了900多个点
然后:
- 导入3d模型文件
- 提取模型顶点数据作为路径
- 对路径点进行排序和处理
- 创建相机移动和旋转动画
- 将动画应用到相机
# 代码实现
- 导入3d模型
import {
Scene,
UniversalCamera,
Vector3,
Mesh,
Texture,
Matrix,
SceneLoader,
VertexBuffer,
MeshBuilder,
Quaternion,
Path3D,
Animation,
AnimationGroup,
TransformNode,
ActionManager,
ExecuteCodeAction
} from "@babylonjs/core";
movingCamera = new UniversalCamera("movingCamera", new Vector3(), scene);
movingCamera.updateUpVectorFromRotation = true;
movingCamera.rotationQuaternion = new Quaternion();
SceneLoader.ImportMesh(
null,
"/models/",
"cameraCurve.glb",
scene,
(meshes) => {
// 找到代表路径的曲线
const curve = scene.getMeshById("curve")
// 将路径模型设置为不可见
curve.isVisible = false
// 提取路径
extractPathPoints(curve)
}
);
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
- 提取路径点数据
function extractPathPoints(mesh) {
// 获取顶点数据
// 顶点数据格式:数组中每3个数字表示一个顶点的坐标(x,y,z) 例如:[x1, y1, z1, x2, y2, z2, ...]
const positions = mesh.getVerticesData(VertexBuffer.PositionKind);
if (!positions) {
console.error("无法获取顶点数据");
return [];
}
// 提取顶点
const worldMatrix = mesh.getWorldMatrix()
let points = [];
// for循环每3个元素取一次,因为每个顶点有x,y,z三个坐标
for (let i = 0; i < positions.length; i += 3) {
// Vector3.TransformCoordinates:将顶点坐标转换到世界坐标系(考虑模型的位置、旋转和缩放)
const position = Vector3.TransformCoordinates(new Vector3(positions[i],positions[i + 1],positions[i + 2]), worldMatrix);
points.push(position)
}
// 路径排序并闭合路径,这个排序算法后面会说
let orderPoints = orderPathPoints(points).reverse()
// 让路径首尾相连
orderPoints.push(orderPoints[0])
// 创建路径
const path = new Path3D(orderPoints)
// 创建动画对象
const frameRate = 30;
// 控制相机位置的动画
const posAnim = new Animation("cameraPos", "position", frameRate, Animation.ANIMATIONTYPE_VECTOR3);
const posKeys = [];
// 控制相机旋转的动画(使用四元数避免旋转问题)
const rotAnim = new Animation("cameraRot", "rotationQuaternion", frameRate, Animation.ANIMATIONTYPE_QUATERNION);
const rotKeys = [];
const time = 120 // 动画总时长(秒)
// 创建动画帧
for (let i = 0; i < time-1; i++) {
// 这个函数会计算每个时间点的相机的位置和旋转
insertFrame(path, i, i, posKeys, rotKeys, time-1)
}
insertFrame(path, 0, time-1, posKeys, rotKeys, time-1)
posAnim.setKeys(posKeys);
rotAnim.setKeys(rotKeys);
movingCamera.animations.push(posAnim);
movingCamera.animations.push(rotAnim);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
路径排序算法
// 路径点排序算法
function orderPathPoints(points) {
// 如果点数量小于等于1,直接返回
if (points.length <= 1) return points;
// 初始化有序数组,从第一个点开始
const ordered = [points[0]];
// 复制剩余点数组,不包含第一个点
const remaining = [...points.slice(1)];
// 循环直到所有点都被排序
while (remaining.length > 0) {
// 获取当前有序数组的最后一个点
const last = ordered[ordered.length - 1];
let closestIndex = 0;
// 初始最小距离设为第一个剩余点与最后点的距离
let minDist = Vector3.Distance(last, remaining[0]);
// 遍历剩余点,找到最近的点
for (let i = 1; i < remaining.length; i++) {
const dist = Vector3.Distance(last, remaining[i]);
// 如果找到更近的点,更新最小距离和索引
if (dist < minDist) {
minDist = dist;
closestIndex = i;
}
}
// 将最近的点添加到有序数组
ordered.push(remaining[closestIndex]);
// 从剩余点数组中移除该点
remaining.splice(closestIndex, 1);
}
return ordered;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
这个算法优点在于:
- 简单易懂
- 适合大多数简单连续路径
- 计算速度快,适合中等数量的点
缺点在于:
- 无法处理交叉路径或分支路径
- 对初始点敏感,如果第一个点选择不当会导致整体路径错误
不过我的路径是环形的并且没有交叉和分支,因此这个算法可以
- 插入动画关键帧
function insertFrame(path, i, frameIndex, posKeys, rotKeys, time) {
// 计算插值比例(0到1之间)
const per = i / time
// 获取路径上的位置和方向
const position = path.getPointAt(per) // 获取路径上指定比例位置的点
const tangent = path.getTangentAt(per) // 获取路径在该点的切线方向,即路径前进方向
const binormal = path.getBinormalAt(per) // 获取路径在该点的副法线方向,即上方向
// 计算相机旋转,确保相机实种沿着路径的切线方向前进,同时保持正确的上下方向
const rotation = Quaternion.FromLookDirectionRH(tangent, binormal);
// 添加关键帧数据
posKeys.push({frame: frameIndex * frameRate, value: position});
rotKeys.push({frame: frameIndex * frameRate, value: rotation});
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
至此动画就写好了,只需要后面调用就可以了
// 运行动画
movingCameraAnimatable = scene.beginAnimation(movingCamera, 0, 60 * 120, true, 1.0);
// 暂停动画
movingCameraAnimatable.pause()
// 停止动画
movingCameraAnimatable.stop()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
