threejs如何自动寻点
更新时间: 2022-04-11 09:35:28
之前做的那个三维编辑器,实现了基本的拖拽模型,布点,今天再加上另一个需求,点击左侧测点列表的时候,摄像头找到对应的测点并且找到最佳的位置观察,效果如下:

# 原理
因为我的测点正好是正方形,所以我的原理就是,找了这个正方形周围的27个点来判断这27个点到测点表面的射线,最后对比哪个点碰到的障碍物少,哪个点就是最佳观测点,然后将摄像头平滑的移到这个点上去。
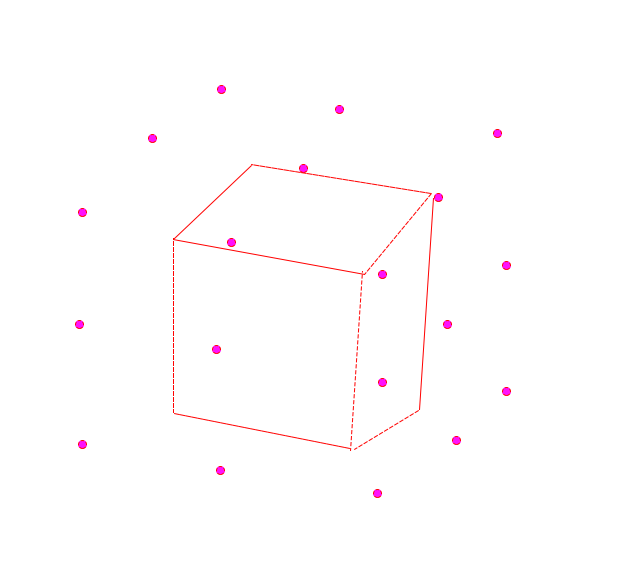
上图所示的就是正方体周围的观测点,由于角度问题,我只展示了正面能看见的几个点。
但是一次循环27个点还是太慢了,因此我们优化一下方法:
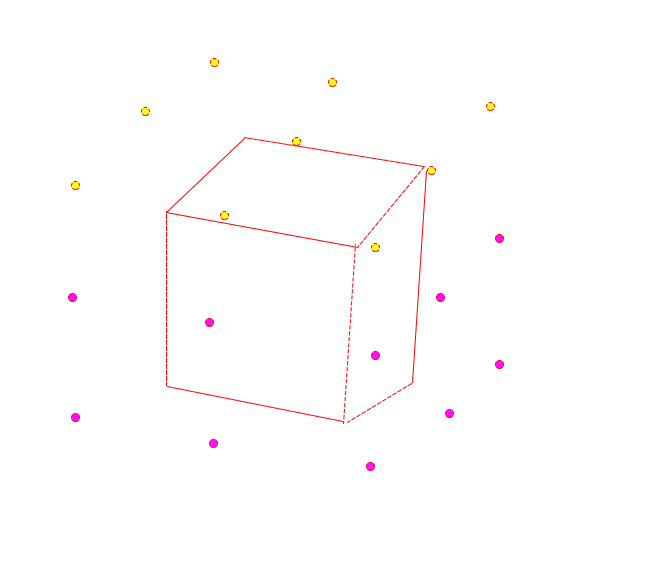
- 首先判断正方体的6个面中哪个面暴露在外没有遮挡
- 然后判断这个面附近的9个观测点的射线就可以了(假设是上面,附近的9个观测点如图中黄点)
- 平滑的将摄像头移动到最佳观测点
# 实现
# 定义6个面的射线检测坐标
首先把6个面的射线检测的起点终点坐标列出来:
// target为目标测点, size为目标测点的大小, distance为检测射线的长度
const facePoints = [
//[每个面正中心的点坐标, 每个面正中心往法线方向distance的坐标]
[[target.x, target.y + size/2, target.z],[target.x, target.y + size/2 + distance * 2, target.z]], //上
[[target.x, target.y, target.z + size/2],[target.x, target.y, target.z + size/2 + distance * 2]], //前
[[target.x, target.y, target.z - size/2],[target.x, target.y, target.z - size/2 - distance * 2]], //后
[[target.x, target.y - size/2, target.z],[target.x, target.y - size/2 - distance * 2, target.z]], //下
[[target.x + size/2, target.y, target.z],[target.x + size/2 + distance * 2, target.y, target.z]], //左
[[target.x - size/2, target.y, target.z],[target.x - size/2 - distance * 2, target.y, target.z]], //右
]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# 定义这6个面对应的9个点
const axisUp = [
[target.x + distance, target.y + distance, target.z + distance], // 左前上角
[target.x + distance, target.y + distance, target.z - distance], //左后上角
[target.x, target.y + distance, target.z], //上方
[target.x - distance, target.y + distance, target.z + distance], // 右前上角
[target.x - distance, target.y + distance, target.z - distance], //右后上角
[target.x, target.y + distance, target.z + distance], //前上方向
[target.x, target.y + distance, target.z - distance], // 后上方向
[target.x + distance, target.y + distance, target.z], //左上方向
[target.x - distance, target.y + distance, target.z], //右上方向
]
const axisDown = [
[target.x + distance, target.y - distance, target.z + distance], // 左前下角
[target.x + distance, target.y - distance, target.z - distance], //左后下角
[target.x, target.y - distance, target.z], //下方
[target.x - distance, target.y - distance, target.z + distance], // 右前下角
[target.x - distance, target.y - distance, target.z - distance], //右后下角
[target.x, target.y - distance, target.z + distance], //前下方向
[target.x, target.y - distance, target.z - distance], // 后下方向
[target.x + distance, target.y - distance, target.z], //左下方向
[target.x - distance, target.y - distance, target.z], //右下方向
]
const axisLeft = [
[target.x + distance, target.y + distance, target.z + distance], // 左前上角
[target.x + distance, target.y + distance, target.z - distance], //左后上角
[target.x + distance, target.y, target.z], //左方
[target.x + distance, target.y - distance, target.z + distance], // 左前下角
[target.x + distance, target.y - distance, target.z - distance], //左后下角
[target.x + distance, target.y + distance, target.z], //左上方向
[target.x + distance, target.y - distance, target.z], //左下方向
[target.x + distance, target.y, target.z + distance], //左前方向
[target.x + distance, target.y, target.z - distance], //左后方向
]
const axisRight = [
[target.x - distance, target.y + distance, target.z + distance], // 右前上角
[target.x - distance, target.y + distance, target.z - distance], //右后上角
[target.x - distance, target.y, target.z], //右方
[target.x - distance, target.y - distance, target.z + distance], // 右前下角
[target.x - distance, target.y - distance, target.z - distance], //右后下角
[target.x - distance, target.y + distance, target.z], //右上方向
[target.x - distance, target.y - distance, target.z], //右下方向
[target.x - distance, target.y, target.z + distance], //右前方向
[target.x - distance, target.y, target.z - distance], //右后方向
]
const axisFront = [
[target.x + distance, target.y + distance, target.z + distance], // 左前上角
[target.x + distance, target.y - distance, target.z + distance], // 左前下角
[target.x, target.y, target.z + distance], //前方
[target.x - distance, target.y + distance, target.z + distance], // 右前上角
[target.x - distance, target.y - distance, target.z + distance], // 右前下角
[target.x + distance, target.y, target.z + distance], //左前方向
[target.x - distance, target.y, target.z + distance], //右前方向
[target.x, target.y + distance, target.z + distance], //前上方向
[target.x, target.y - distance, target.z + distance], //前下方向
]
const axisBack = [
[target.x + distance, target.y + distance, target.z - distance], // 左后上角
[target.x + distance, target.y - distance, target.z - distance], // 左后下角
[target.x, target.y, target.z - distance], //后方
[target.x - distance, target.y + distance, target.z - distance], // 右后上角
[target.x - distance, target.y - distance, target.z - distance], // 右后下角
[target.x + distance, target.y, target.z - distance], //左后方向
[target.x - distance, target.y, target.z - distance], //右后方向
[target.x, target.y + distance, target.z - distance], //后上方向
[target.x, target.y - distance, target.z - distance], //后下方向
]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
# 如何进行两点间的射线检测
首先来看下Raycaster构造器:
Raycaster( origin : Vector3, direction : Vector3, near : Float, far : Float )
- origin —— 光线投射的原点向量。
- direction —— 向射线提供方向的方向向量,应当被标准化。
- near —— 返回的所有结果比near远。near不能为负值,其默认值为0。
- far —— 返回的所有结果都比far近。far不能小于near,其默认值为Infinity(正无穷。)
// 计算两点之间的射线
function raycaster2Point(startPoint, endPoint, near = 0, model) {
const vectorStr = new THREE.Vector3(startPoint[0], startPoint[1], startPoint[2]);
const vectorEnd = new THREE.Vector3(endPoint[0], endPoint[1], endPoint[2]);
const vectorEnd1 = new THREE.Vector3(endPoint[0], endPoint[1], endPoint[2]);
const raycaster = new THREE.Raycaster(vectorStr, vectorEnd.sub(vectorStr).normalize(), near, vectorEnd1.distanceTo(vectorStr))
const intersects = raycaster.intersectObjects(model, true);
return intersects
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# 判断正方体外露面
let min = 0
let outsideIndex = 0
// 首先判断正方形哪个面露在外面
for( let i = 0; i < facePoints.length; i++) {
const intersects = raycaster2Point(facePoints[i][0], facePoints[i][1], 0, scene.children);
if(i == 0) {
min = intersects.length
outsideIndex = i
}else {
if(intersects.length < min ) {
min = intersects.length
outsideIndex = i
}
}
if(min == 0) {
break
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
# 判断最佳观测点
let returnAxis = [0, 0, 0]
switch(outsideIndex) {
case 0: //上
// 假如是上面的话优先判断上方一圈
returnAxis = countBestPoint(facePoints[0][0], axisUp, distance)
break;
case 1: //前
// 假如是前面的话优先判断前面一圈
returnAxis = countBestPoint(facePoints[1][0], axisFront, distance)
break;
case 2: //后
// 假如是后面的话优先判断后面一圈
returnAxis = countBestPoint(facePoints[2][0], axisBack, distance)
break;
case 3: //下
// 假如是下面的话优先判断下方一圈
returnAxis = countBestPoint(facePoints[3][0], axisDown, distance)
break;
case 4: //左
// 假如是左边的话优先判断左边一圈
returnAxis = countBestPoint(facePoints[4][0], axisLeft, distance)
break;
case 5: //右
// 假如是右边的话优先判断右边一圈
returnAxis = countBestPoint(facePoints[5][0], axisRight, distance)
break;
}
function countBestPoint(startPoint, pointList, distance) {
let objectMin = 0
let result = []
for(let j = 0;j < pointList.length; j++) {
const intersects = raycaster2Point(startPoint, pointList[j] , 0, scene.children)
if(j == 0) {
objectMin = intersects.length
result = pointList[j]
}else {
if(intersects.length < objectMin ) {
objectMin = intersects.length
result = pointList[j]
}
}
if(objectMin == 0) {
break
}
}
return result
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
returnAxis 就是最佳观测点
# 将摄像头平滑的移动到指定的位置
使用tween.js来平滑过渡
// target是目标测点的位置, position是摄像头将要移动到的位置
function moveCamera(target,position) {
let positionVar = {
x1: camera.position.x,
y1: camera.position.y,
z1: camera.position.z,
x2: orbitControls.target.x,
y2: orbitControls.target.y,
z2: orbitControls.target.z
};
//关闭控制器
orbitControls.enabled = false;
let tween = new TWEEN.Tween(positionVar);
tween.to({
x1: position.x,
y1: position.y,
z1: position.z,
x2: target.x,
y2: target.y,
z2: target.z
}, 1000);
tween.onUpdate(function() {
camera.position.x = positionVar.x1;
camera.position.y = positionVar.y1;
camera.position.z = positionVar.z1;
orbitControls.target.x = positionVar.x2;
orbitControls.target.y = positionVar.y2;
orbitControls.target.z = positionVar.z2;
orbitControls.update();
})
tween.onComplete(function() {
///开启控制器
orbitControls.enabled = true;
})
tween.easing(TWEEN.Easing.Cubic.InOut);
tween.start();
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
记得要在动画循环中加上:
TWEEN.update()
这样动画才能动起来哦!
